Introduction to MS-Excel
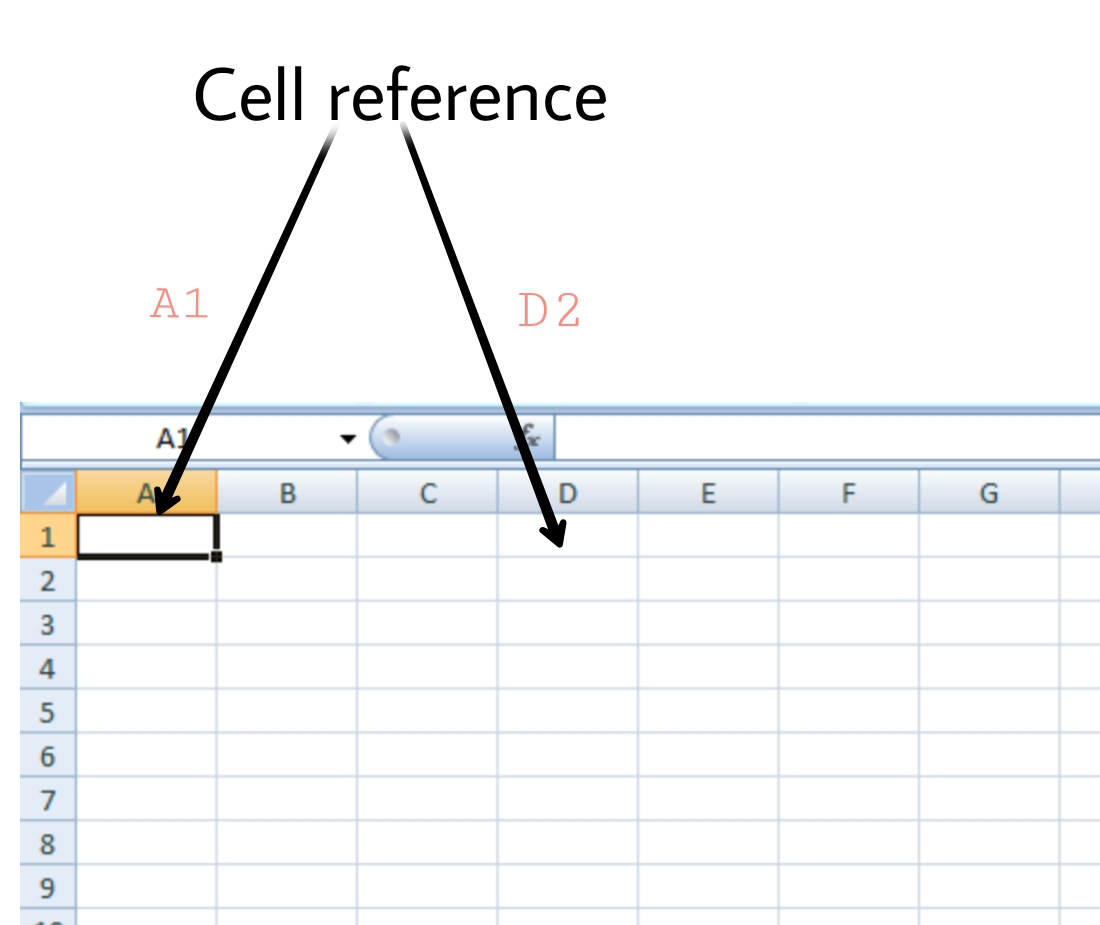
MS-EXCEL is a part of Microsoft Office suite software. It is an electronic spreadsheet with numerous rows and columns, used for organizing data, graphically represent data(s), and performing different calculations. It consists of 1048576 rows and 16384 columns, a row and column together make a cell. Each cell has an address defined by column name and row number example A1, D2, etc. this is also known as a cell reference.
The best part about Excel is, that it can apply to many business tasks, including statistics, finance, data management, forecasting, analysis, tracking inventory & billing, and business intelligence. Following are the few things which it can do for you:
- Number Crunching
- Charts and Graphs
- Store and Import Data
- Manipulating Text
- Templates/Dashboards
- Automation of Tasks
- And Much More…
The three most important components of Excel you need to understand first:
Cell
A cell is a smallest but most powerful part of a spreadsheet. You can enter your data into a cell either by typing or by copy-paste.
Data can be a text, a number, or a date. You can also customize it by changing its size, font color, background color, borders, etc.
Every cell is identified by its cell address, cell address contains its column number and row number (If a cell is on the 11th row and on column AB, then its address will be AB11).
Worksheet
A worksheet is made up of individual cells which can contain a value, a formula, or text. It also has an invisible draw layer, which holds charts, images, and diagrams.
Each worksheet in a workbook is accessible by clicking the tab at the bottom of the workbook window.
In addition, a workbook can store chart sheets; a chart sheet displays a single chart and is accessible by clicking a tab.
Workbook
A workbook is a separate file just like every other application has. Each workbook contains one or more worksheets.
You can also say that a workbook is a collection of multiple worksheets or can be a single worksheet.
You can add or delete worksheets, hide them within the workbook without deleting them, and change the order of your worksheets within the workbook.

- Active Cell – A cell that is currently selected. It will be highlighted by a rectangular box and its address will be shown in the address bar. You can activate a cell by clicking on it or by using your arrow buttons. To edit a cell, you double-click on it or use F2 as well.
- Column – A column is a vertical set of cells. A single worksheet contains 16384 total columns. Every column has its own alphabet for identity, from A to XFD. You can select a column by clicking on its header.
- Row – A row is a horizontal set of cells. A single worksheet contains 1048576 total rows. Every row has its own number for identity, starting from 1 to 1048576. You can select a row by clicking on the row number marked on the left side of the window.
- Fill Handle – It’s a small dot present in the lower right corner of the active cell. It helps you to fill numeric values, text series, insert ranges, insert serial numbers, etc.
- Address Bar – It shows the address of the active cell. If you have selected more than one cell, then it will show the address of the first cell in the range.
- Formula Bar – The formula bar is an input bar, below the ribbon. It shows the content of the active cell, and you can also use it to enter a formula in a cell.
- Title Bar – The title bar will show the name of your workbook, followed by the application name (“Microsoft Excel”).
- File Menu – The file menu is a simple menu like all other applications. It contains options like (Save, Save As, Open, New, Print, Excel Options, Share, etc).
- Quick Access Toolbar – A toolbar to quickly access the options which you frequently use. You can add your favorite options by adding new options to the quick access toolbar.
- Ribbon – Starting from Microsoft Excel 2007, all the options menus are replaced with ribbons. Ribbon tabs are a bunch of specific option group which further contains the option.
- Worksheet Tab – This tab shows all the worksheets which are present in the workbook. By default, you will see, three worksheets in your new workbook with the names Sheet1, Sheet2, and Sheet3 respectively.
- Status Bar – It is a thin bar at the bottom of the Excel window. It will give you instant help once you start working in Excel.
Cell references: The address or name of a cell or a range of cells is known as Cell reference. It helps the software to identify the cell from where the data/value is to be used in the formula. We can reference the cell of other worksheets and also of other programs.
- Referencing the cell of other worksheets is known as External referencing.
- Referencing the cell of other programs is known as Remote referencing.
There are three types of cell references in Excel:
- Relative reference.
- Absolute reference.
- Mixed reference.
The Ribbon in MS-Excel is the topmost row of tabs that provide the user with different facilities/functionalities. These tabs are:

- Home Tab: It provides the basic facilities like changing the font, size of text, editing the cells in the spreadsheet, autosum, etc.
- Insert Tab: It provides the facilities like inserting tables, pivot tables, images, clip art, charts, links, etc.
- Page layout: It provides all the facilities related to the spreadsheet-like margins, orientation, height, width, background etc. The worksheet appearance will be the same in the hard copy as well.
- Formulas: It is a package of different in-built formulas/functions which can be used by user just by selecting the cell or range of cells for values.
- Data: The Data Tab helps to perform different operations on a vast set of data like analysis through what-if analysis tools and many other data analysis tools, removing duplicate data, transpose the row and column, etc. It also helps to access data(s) from different sources as well, such as from Ms-Access, from web, etc.
- Review: This tab provides the facility of thesaurus, checking spellings, translating the text, and helps to protect and share the worksheet and workbook.
- View: It contains the commands to manage the view of the workbook, show/hide ruler, gridlines, etc, freezing panes, and adding macros.
Creating a new spreadsheet:
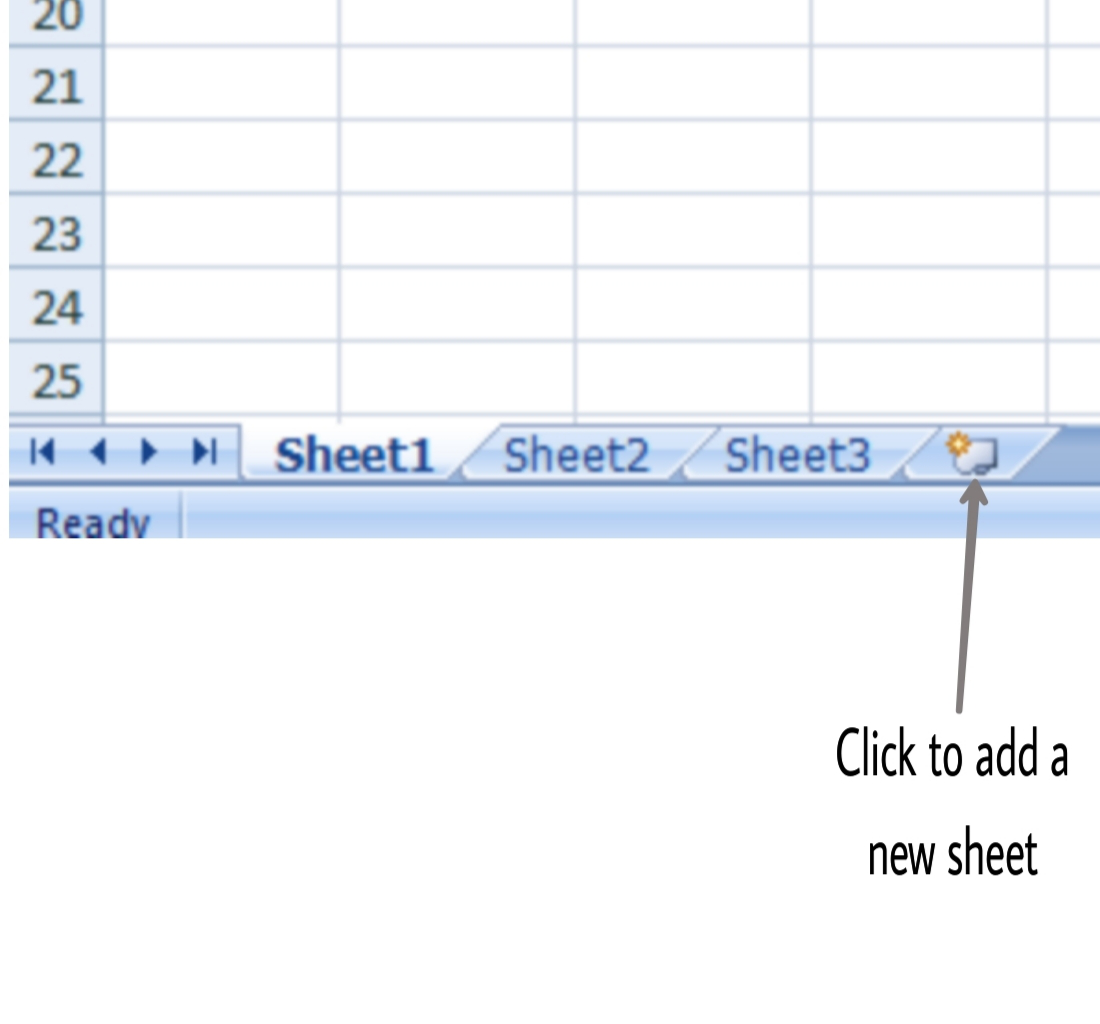
In Excel 3 sheets are already opened by default, now to add a new sheet :
- In the lowermost pane in Excel, you can find a button.
- Click on that button to add a new sheet.
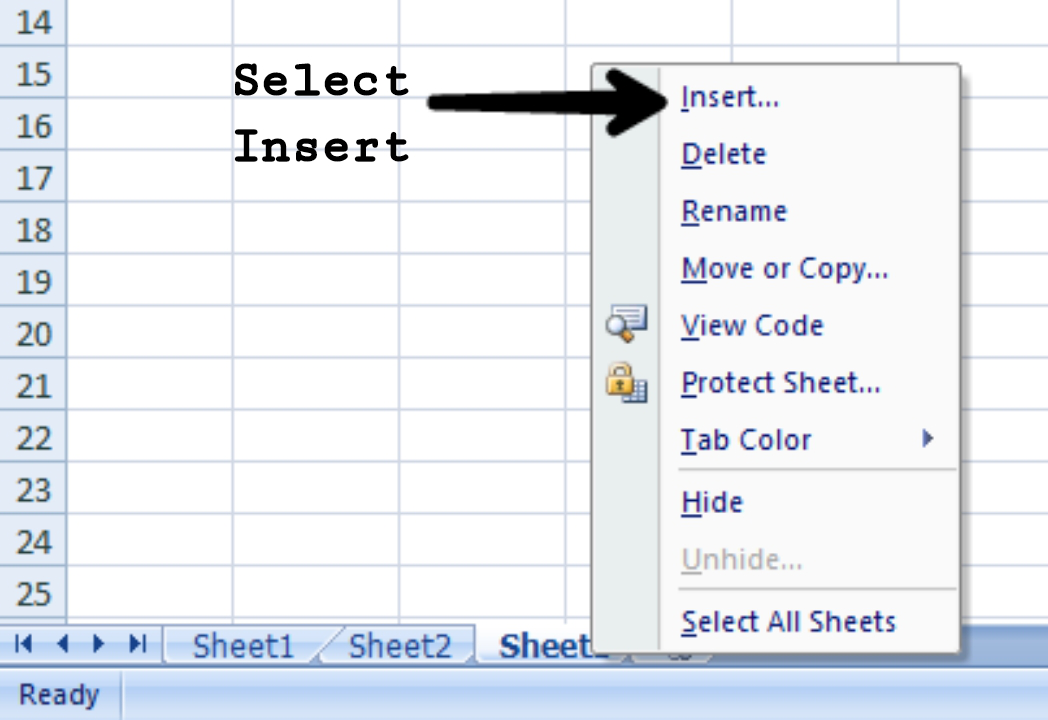
- We can also achieve the same by Right-clicking on the sheet number before which you want to insert the sheet.
- Click on Insert.
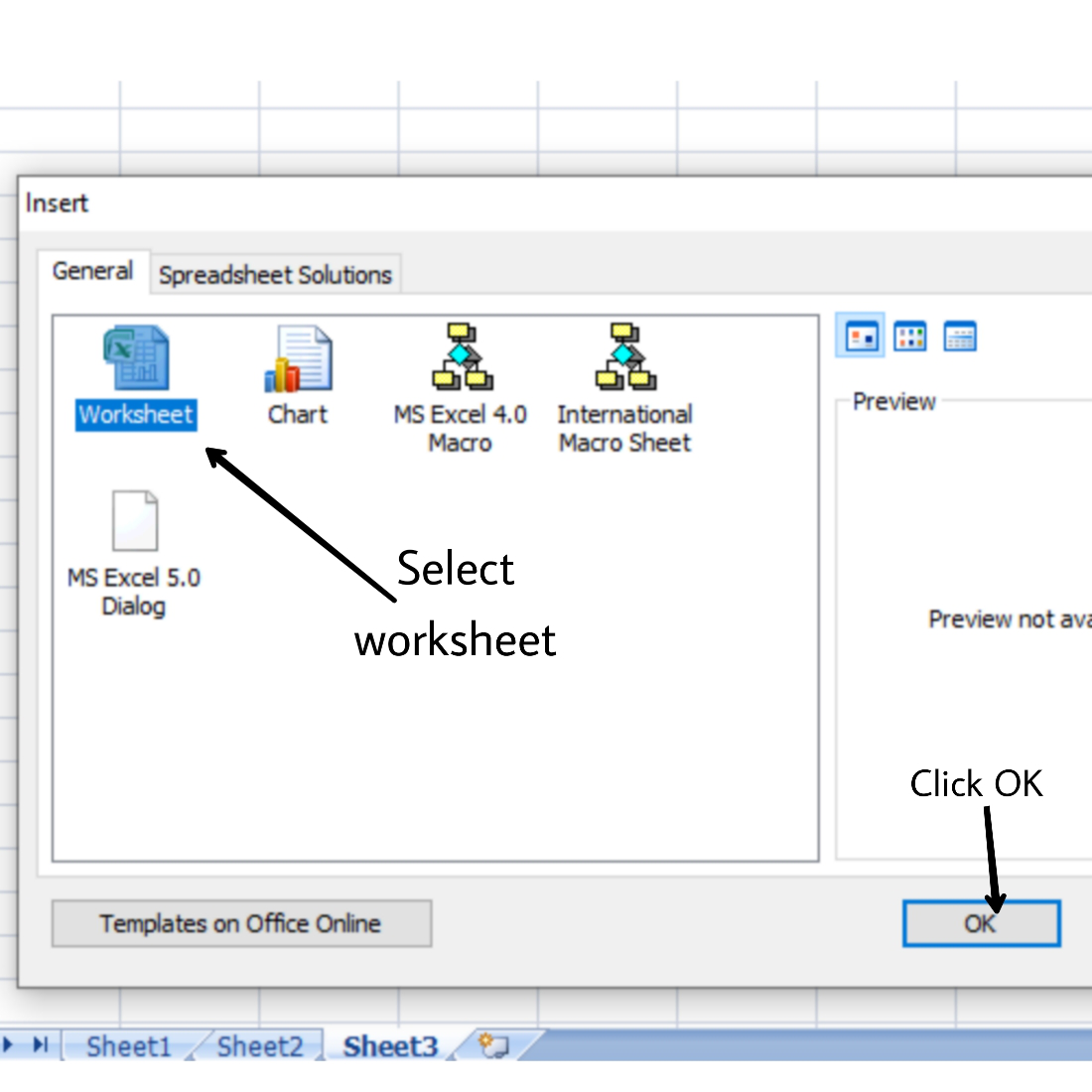
- Select Worksheet.
- Click OK.
Opening previous spreadsheet:
On the lowermost pane in Excel, you can find the name of the current sheet you have opened.
On the left side of this sheet, the name of previous sheets are also available like Sheet 2, Sheet 3 will be available at the left of sheet4, click on the number/name of the sheet you want to open and the sheet will open in the same workbook.
For example, we are on Sheet 4, and we want to open Sheet 2 then simply just click on Sheet2 to open it.

Managing the spreadsheets:
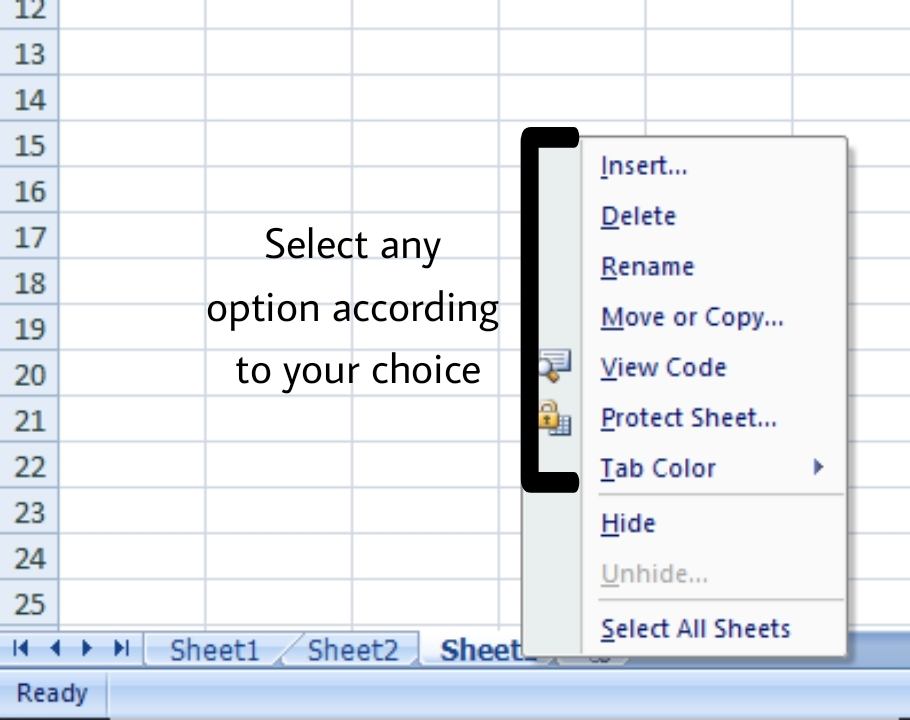
You can easily manage the spreadsheets in Excel simply by :
- Simply navigating between the sheets.

- Right-clicking on the sheet name or number on the pane.
- Choose among the various options available like, move, copy, rename, add, delete etc.
- You can move/copy your sheet to other workbooks as well just by selecting the workbook in the To workbook and the sheet before you want to insert the sheet in Before sheet.
To save the workbook:
- Click on the Office Button or the File tab.
- Click on Save As option.
- Write the desired name of your file.
- Click OK.
To share your workbook:
- Click on the Review tab on the Ribbon.
- Click on the share workbook (under Changes group).
- If you want to protect your workbook and then make it available for another user then click on Protect and Share Workbook option.
- Now check the option “Allow changes by more than one user at the same time. This also allows workbook merging” in the Share Workbook dialog box.
- Many other options are also available in the Advanced like track, update changes.
- Click OK.
Ms-Excel shortcuts:
- Ctrl+N: To open a new workbook.
- Ctrl+O: To open a saved workbook.
- Ctrl+S: To save a workbook.
- Ctrl+C: To copy the selected cells.
- Ctrl+V: To paste the copied cells.
- Ctrl+X: To cut the selected cells.
- Ctrl+W: To close the workbook.
- Delete: To remove all the contents from the cell.
- Ctrl+P: To print the workbook.
- Ctrl+Z: To undo.





No comments:
Post a Comment