Smart Computer Educational Trust.
Microsoft word is a word processor software developed by Microsoft in 1983.
It is the most commonly used word processor software. It is used to create professional quality documents, letters, reports, resumes, etc and also allows you to edit or modify your new or existing document.
The file
saved in Ms Word has .docx extension. It is a component of the Microsoft Office
suite, but you can buy it separately and is available for both Windows and
macOS. The latest version of Ms Word is 2019. In this article we will learn the
features of Ms Word, but first we learn how to open Ms Word?
Brief History
Microsoft word was released in 1983 as Multi-Tool Word. Its first version was based on the framework of Bravo which was world's first graphical writing program.
Microsoft renamed Multi Tool Word to Microsoft Word, and then in October 1983, Microsoft released its first version for the IBM PC.
In 1985, Microsoft ported it to the Macintosh which was different from its DOS-based counterpart, i.e. Macintosh offered various major interface changes.
In 1989, Microsoft released a new version of Word for its Windows operating systems. It was the Microsoft Word who introduced the concept of WYSIWYG (What You See Is What You Get), i.e. it allowed to create and display bold and italics text.
In 2014, Microsoft developed the source code for Microsoft Word for Windows 1.1a.
Learning objectives
•
Indicate the names and functions of the Word interface components.
•
Create, edit, save, and print documents to include documents with lists
and tables.
•
Format text and to use styles.
•
Add a header and footer to a document.
•
Add a footnote to a document.
• Add a graphic to a document.
Keywords
•
Cut the current selection: Ctrl + X.
•
Copy the current selection: Ctrl + C.
•
Paste the contents of the clipboard: Ctrl + V.
•
Bold: Ctrl + B.
•
Italics: Ctrl + I.
•
Underline: Ctrl + U.
•
Underline words only: Ctrl + Shift + W.
•
Center: Ctrl + E.
Standards
•
Keep It Simple, Less Is More. ...
•
Choose a Context-Appropriate Typeface. ...
•
Use Standard Font Size and Color. ...
•
Use Standard Page Size and Margins. ...
•
Align Paragraphs to the Left. ...
•
Indent the First Lines of Paragraphs. ...
•
Place Images Between Paragraphs
Opening Interface of Ms-Word
Quick Access Toolbar lies next to the Microsoft Office Button. It is a customizable toolbar that comes with a set of independent commands. It gives you quick access to commonly used commands such as Save, Undo, Redo, etc.
See the image:

When you click the drop-down arrow next to toolbar it offers more commands. With a left click you can add any of these commands to Quick Access Toolbar. You can also remove the commands added to the tool bar. The indent, spacing values, individual styles and other features that appear on the ribbon cannot be added to quick access toolbar. The following image is showing the menu of quick access toolbar.
Title Bar
It lies next to the Quick Access Toolbar. It displays the title of the currently open document or application. It is present on almost all windows displayed on your computer. So, if there are several windows across the screen, you can identify each window by looking at the title bar. In many graphical user interfaces, you can also move a window by dragging the title bar.
See the image:

Ribbon and Tabs
The Ribbon is a user interface element which was introduced by Microsoft in Microsoft Office 2007. It is located below the Quick Access Toolbar and the Title Bar. It comprises seven tabs; Home, Insert, Page layout, References, Mailing, Review and View. Each tab has specific groups of related commands. It gives you quick access to the commonly used commands that you need to complete a task.
See the image:

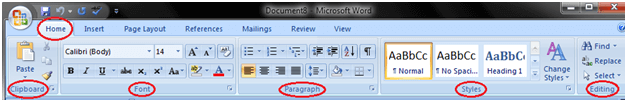
Home tab:
The Home tab is the default tab in Microsoft Word. It has five groups of related commands; Clipboard, Font, Paragraph, Styles and Editing. It helps you change document settings like font size, adding bullets, adjusting styles and many other common features. It also helps you to return to the home section of the document.
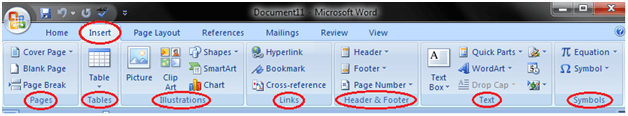
Insert tab:
Insert Tab is the second tab in the Ribbon. As the name suggests, it is used to insert or add extra features in your document. It is commonly used to add tables, pictures, clip art, shapes, page number, etc. The Insert tab has seven groups of related commands; Pages, Tables, Illustrations, Links, Header & Footer, Text and Symbols.
See the image:
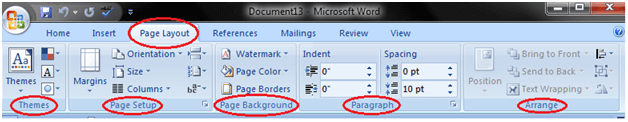
Page Layout tab:
It is the third tab in the Ribbon. This tab allows you to control the look and feel of your document, i.e. you can change the page size, margins, line spacing, indentation, documentation orientation, etc. The Page Layout tab has five groups of related commands; Themes, Page Setup, Page Background, Paragraph and Arrange.
See the image:













No comments:
Post a Comment